Cusabio Polyclonal Antibodies
AKR7A2 Antibody | CSB-PA001550ESR1HU
- SKU:
- CSB-PA001550ESR1HU
- Availability:
- 3 to 7 Working Days
Description
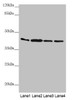
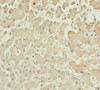
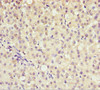
AKR7A2 Antibody | CSB-PA001550ESR1HU | Cusabio
AKR7A2 Antibody is Available at Gentaur Genprice with the fastest delivery.
Online Order Payment is possible or send quotation to info@gentaur.com.
Product Type: Polyclonal Antibody
Target Names: AKR7A2
Aliases: Aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductase member 2 (EC 1.1.1.n11) (AFB1 aldehyde reductase 1) (AFB1-AR 1) (Aldoketoreductase 7) (Succinic semialdehyde reductase) (SSA reductase), AKR7A2, AFAR AFAR1 AKR7
Background: Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of succinic semialdehyde to gamma-hydroxybutyrate. May have an important role in producing the neuromodulator gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) . Has broad substrate specificity. Has NADPH-dependent aldehyde reductase activity towards 2-carboxybenzaldehyde, 2-nitrobenzaldehyde and pyridine-2-aldehyde (in vitro) . Can reduce 1, 2-naphthoquinone and 9, 10-phenanthrenequinone (in vitro) . Can reduce the dialdehyde protein-binding form of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) to the non-binding AFB1 dialcohol. May be involved in protection of liver against the toxic and carcinogenic effects of AFB1, a potent hepatocarcinogen.
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Non-conjugated
Clonality: Polyclonal
Uniport ID: O43488
Host Species: Rabbit
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Immunogen: Recombinant Human Aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductase member 2 protein (100-359AA)
Immunogen Species: Human
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Tested Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC; Recommended dilution: WB:1:1000-1:5000, IHC:1:20-1:200
Purification Method: Antigen Affinity Purified
Dilution Ratio1: ELISA:1:2000-1:10000
Dilution Ratio2: WB:1:1000-1:5000
Dilution Ratio3: IHC:1:20-1:200
Dilution Ratio4:
Dilution Ratio5:
Dilution Ratio6:
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Form: Liquid
Storage: Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Initial Research Areas: Signal Transduction
Research Areas: Neuroscience;Cancer;Metabolism;Signal transduction