Cusabio Polyclonal Antibodies
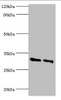
KCTD15 Antibody | CSB-PA836301ESR2HU
- SKU:
- CSB-PA836301ESR2HU
- Availability:
- 3 to 7 Working Days
Description
KCTD15 Antibody | CSB-PA836301ESR2HU | Cusabio
KCTD15 Antibody is Available at Gentaur Genprice with the fastest delivery.
Online Order Payment is possible or send quotation to info@gentaur.com.
Product Type: Polyclonal Antibody
Target Names: KCTD15
Aliases: BTB/POZ domain-containing protein KCTD15 (Potassium channel tetramerization domain-containing protein 15), KCTD15
Background: During embryonic development, interferes with neural crest formation (By similarity) . Inhibits AP2 transcriptional activity by interaction with its activation domain.
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Non-conjugated
Clonality: Polyclonal
Uniport ID: Q96SI1
Host Species: Rabbit
Species Reactivity: Human
Immunogen: Recombinant Human BTB/POZ domain-containing protein KCTD15 protein (1-234AA)
Immunogen Species: Human
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Tested Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC; Recommended dilution: WB:1:500-1:2000, IHC:1:20-1:200
Purification Method: Antigen Affinity Purified
Dilution Ratio1: ELISA:1:2000-1:10000
Dilution Ratio2: WB:1:500-1:2000
Dilution Ratio3: IHC:1:20-1:200
Dilution Ratio4:
Dilution Ratio5:
Dilution Ratio6:
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Form: Liquid
Storage: Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Initial Research Areas: Neuroscience
Research Areas: Neuroscience;Metabolism;Signal transduction