Cusabio Polyclonal Antibodies
KCNK1 Antibody | CSB-PA012062LA01HU
- SKU:
- CSB-PA012062LA01HU
- Availability:
- 3 to 7 Working Days
Description
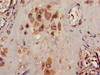
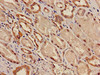
KCNK1 Antibody | CSB-PA012062LA01HU | Cusabio
KCNK1 Antibody is Available at Gentaur Genprice with the fastest delivery.
Online Order Payment is possible or send quotation to info@gentaur.com.
Product Type: Polyclonal Antibody
Target Names: KCNK1
Aliases: Potassium channel subfamily K member 1 (Inward rectifying potassium channel protein TWIK-1) (Potassium channel K2P1) (Potassium channel KCNO1), KCNK1, HOHO1 KCNO1 TWIK1
Background: Ion channel that contributes to passive transmembrane potassium transport and to the regulation of the resting membrane potential in brain astrocytes, but also in kidney and in other tissues (PubMed:15820677, PubMed:21653227) . Forms dimeric channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel is selective for K (+) ions at physiological potassium concentrations and at neutral pH, but becomes permeable to Na (+) at subphysiological K (+) levels and upon acidification of the extracellular medium (PubMed:21653227, PubMed:22431633) . The homodimer has very low potassium channel activity, when expressed in heterologous systems, and can function as weakly inward rectifying potassium channel (PubMed:8605869, PubMed:8978667, PubMed:15820677, PubMed:21653227, PubMed:22431633, PubMed:23169818, PubMed:25001086) . Channel activity is modulated by activation of serotonin receptors (By similarity) . Heterodimeric channels containing KCNK1 and KCNK2 have much higher activity, and may represent the predominant form in astrocytes (By similarity) . Heterodimeric channels containing KCNK1 and KCNK3 or KCNK9 have much higher activity (PubMed:23169818) . Heterodimeric channels formed by KCNK1 and KCNK9 may contribute to halothane-sensitive currents (PubMed:23169818) . Mediates outward rectifying potassium currents in dentate gyrus granule cells and contributes to the regulation of their resting membrane potential (By similarity) . Contributes to the regulation of action potential firing in dentate gyrus granule cells and down-regulates their intrinsic excitability (By similarity) . In astrocytes, the heterodimer formed by KCNK1 and KCNK2 is required for rapid glutamate release in response to activation of G-protein coupled receptors, such as F2R and CNR1 (By similarity) . Required for normal ion and water transport in the kidney (By similarity) . Contributes to the regulation of the resting membrane potential of pancreatic beta cells (By similarity) . The low channel activity of homodimeric KCNK1 may be due to sumoylation (PubMed:15820677, PubMed:20498050, PubMed:23169818) . The low channel activity may be due to rapid internalization from the cell membrane and retention in recycling endosomes (PubMed:19959478) .
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Non-conjugated
Clonality: Polyclonal
Uniport ID: O00180
Host Species: Rabbit
Species Reactivity: Human
Immunogen: Recombinant Human Potassium channel subfamily K member 1 protein (268-336AA)
Immunogen Species: Human
Applications: ELISA, IHC, IF
Tested Applications: ELISA, IHC, IF; Recommended dilution: IHC:1:20-1:200, IF:1:50-1:200
Purification Method: >95%, Protein G purified
Dilution Ratio1: ELISA:1:2000-1:10000
Dilution Ratio2: IHC:1:20-1:200
Dilution Ratio3: IF:1:50-1:200
Dilution Ratio4:
Dilution Ratio5:
Dilution Ratio6:
Buffer: Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4
Form: Liquid
Storage: Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Initial Research Areas: Neuroscience
Research Areas: Neuroscience;Metabolism;Signal transduction