By using genetic data to deliver accurate and customized therapies, genomic medicine transforms healthcare. This area of study has several uses, ranging from determining genetic risk factors for illness to creating personalized treatments according to a person's genetic makeup.

One of the key aspects of genomic medicine is the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies. NGS enables the rapid and cost-effective sequencing of an individual's entire genome or specific regions of interest. This technology has significantly advanced our understanding of the genetic basis of disease by allowing researchers and clinicians to identify genetic variants associated with disease risk.
In clinical practice, genomic medicine is used to diagnose and manage a variety of diseases, including cancer and rare genetic disorders. For example, in cancer treatment, genomic testing can identify specific mutations in a patient's tumor that can be targeted with personalized therapies, such as targeted drugs or immunotherapy.
Genomic medicine also plays a crucial role in preventive medicine. By identifying individuals at increased risk for certain diseases based on their genetic profile, healthcare providers can offer personalized screening and preventive measures to reduce the risk of disease development.
Furthermore, genomic medicine is advancing the field of pharmacogenomics, which aims to optimize drug therapy based on an individual's genetic makeup. By understanding how an individual's genes affect their response to medications, healthcare providers can tailor drug dosages and selection to maximize effectiveness and minimize side effects.
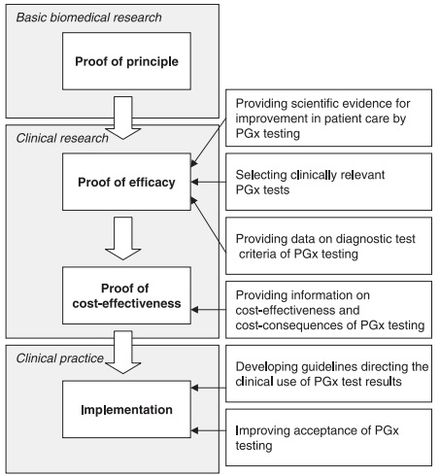
Overall, genomic medicine holds great promise for improving patient outcomes and revolutionizing healthcare by providing personalized and precise treatments tailored to each individual's genetic makeup.
For more information , click here
