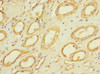
Cusabio Polyclonal Antibodies
EPHB4 Antibody | CSB-PA007732ESR2HU
- SKU:
- CSB-PA007732ESR2HU
- Availability:
- 3 to 7 Working Days
Description
EPHB4 Antibody | CSB-PA007732ESR2HU | Cusabio
EPHB4 Antibody is Available at Gentaur Genprice with the fastest delivery.
Online Order Payment is possible or send quotation to info@gentaur.com.
Product Type: Polyclonal Antibody
Target Names: EPHB4
Aliases: Ephrin type-B receptor 4 (EC 2.7.10.1) (Hepatoma transmembrane kinase) (Tyrosine-protein kinase TYRO11), EPHB4, HTK MYK1 TYRO11
Background: Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously transmembrane ephrin-B family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Together with its cognate ligand/functional ligand EFNB2 plays a central role in heart morphogenesis and angiogenesis through regulation of cell adhesion and cell migration. EPHB4-mediated forward signaling controls cellular repulsion and segregation form EFNB2-expressing cells. Plays also a role in postnatal blood vessel remodeling, morphogenesis and permeability and is thus important in the context of tumor angiogenesis.
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Non-conjugated
Clonality: Polyclonal
Uniport ID: P54760
Host Species: Rabbit
Species Reactivity: Human
Immunogen: Recombinant Human Ephrin type-B receptor 4 protein (300-540AA)
Immunogen Species: Human
Applications: ELISA, IHC
Tested Applications: ELISA, IHC; Recommended dilution: IHC:1:20-1:200
Purification Method: Antigen Affinity Purified
Dilution Ratio1: ELISA:1:2000-1:10000
Dilution Ratio2: IHC:1:20-1:200
Dilution Ratio3:
Dilution Ratio4:
Dilution Ratio5:
Dilution Ratio6:
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Form: Liquid
Storage: Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Initial Research Areas: Cardiovascular
Research Areas: Neuroscience;Cardiovascular;Stem cells