Cusabio Polyclonal Antibodies
ATP5H Antibody | CSB-PA002366ESR2HU
- SKU:
- CSB-PA002366ESR2HU
- Availability:
- 3 to 7 Working Days
Description
ATP5H Antibody | CSB-PA002366ESR2HU | Cusabio
ATP5H Antibody is Available at Gentaur Genprice with the fastest delivery.
Online Order Payment is possible or send quotation to info@gentaur.com.
Product Type: Polyclonal Antibody
Target Names: ATP5H
Aliases: ATP synthase subunit d, mitochondrial (ATPase subunit d), ATP5H
Background: Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F (1) F (0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F (1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core, and F (0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F (1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F (0) domain and the peripheric stalk, which acts as a stator to hold the catalytic alpha (3) beta (3) subcomplex and subunit a/ATP6 static relative to the rotary elements.
Isotype: IgG
Conjugate: Non-conjugated
Clonality: Polyclonal
Uniport ID: O75947
Host Species: Rabbit
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
Immunogen: Recombinant Human ATP synthase subunit d, mitochondrial protein (1-161AA)
Immunogen Species: Human
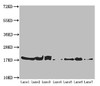
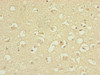
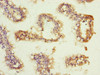
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Tested Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC; Recommended dilution: WB:1:1000-1:5000, IHC:1:20-1:200
Purification Method: Antigen Affinity Purified
Dilution Ratio1: ELISA:1:2000-1:10000
Dilution Ratio2: WB:1:1000-1:5000
Dilution Ratio3: IHC:1:20-1:200
Dilution Ratio4:
Dilution Ratio5:
Dilution Ratio6:
Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
Form: Liquid
Storage: Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Initial Research Areas: Tags & Cell Markers
Research Areas: Cancer;Tags & Cell Markers;Metabolism;Signal transduction